Chain Transactions
Chain transactions, also called ABC Contracts or Drop Shipment, are a series of sales where the goods are shipped from the first seller to the final customer.
Triangulation is a special regime in the EU that applies to qualifying chain transactions. In triangulation, all countries in the transaction are different EU member states, registered in their own country. Chain transaction is a broader term that includes triangulation.
For more detail about these transactions, see:
Using Authority Options to Implement Taxation Rules
Because EU countries have different conditions for chain transactions and triangulation simplification, two Authority Options allow you to implement the rules of each country. Each country can have different conditions for triangulation with regard to Registration and Establishment, since a single chain transaction could involve countries with conflicting rules.
Triangulation Simplification allows each country to have different triangulation conditions for Registration and Establishment. You can set a Triangulation Simplification authority option to specify how you want transactions evaluated.
For example, a value of Always applies simplification rules regardless of registration and establishment; Not Applicable applies no simplification rules, regardless of registration and establishment.
Chain Transaction Transportation allows you to set the impact of the party responsible for the transport of goods (delivery terms) to be considered differently for each country. This is particularly important when the final customer is responsible for the transport (picks up the goods at the seller's location). These pick-ups are identified with a POTT of "Origin."
For more information about these two authority options, see Advanced Authority Configuration.
Country specific rules and two authority options allow you to customize the system according to your own policy. This may be useful when dealing with chain transactions because a single chain could involve countries with conflicting rules.
A chain transaction is defined as:
- A sale of goods.
- Three or more taxable persons in at least three different locations.
- Locations are not required to all be in the EU.
- There are two sale transactions: B to C (T1) and A to B (T2).
- One transport is directly from A to C, either ship or pickup.
To compare triangulation simplification to chain transactions, see Triangulation Simplification.
Chain Transaction Example
The following illustration shows a Chain Transaction and a Goods Transaction:
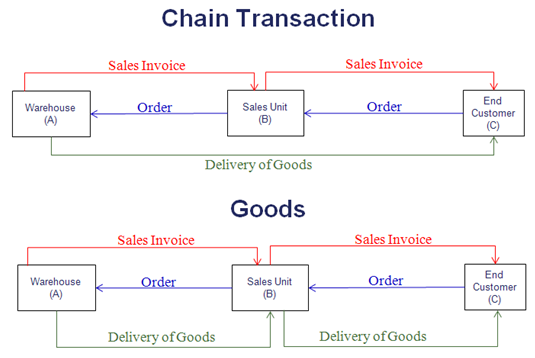
Transaction Types and Transportation Responsibility
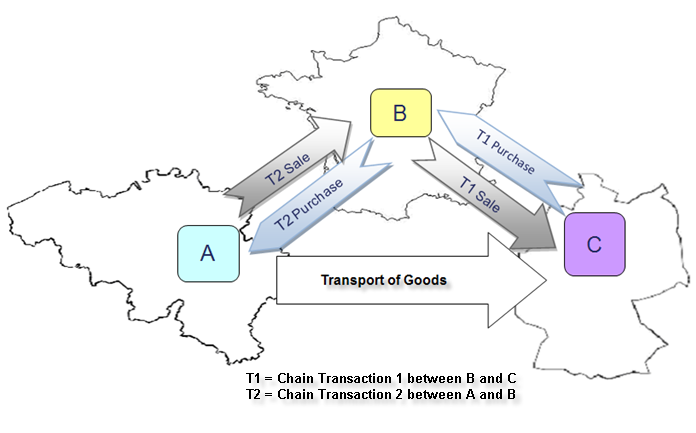
Because a chain transaction with three parties has two different transactions, Chain Transaction 1 (T1) and Chain Transaction 2 (T2) transaction types allow you to identify transactions for each leg of the triangle, as shown in this illustration.
The following table explains the relationship between transaction type and company role:
|
Transaction Type and Company Role |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Role |
Transaction Type |
|
Company A - Sales Invoice |
Seller |
Chain Transaction 2 |
|
Company B - Sales Invoice |
Seller or Middleman |
Chain Transaction 1 |
|
Company B - Purchase Order |
Buyer or Middleman |
Chain Transaction 2 |
This table shows the impact of transaction type and delivery terms in Intra-EC Transactions:
|
Intra-EC Transactions |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Delivery Terms |
Chain Transaction 1 |
Chain Transaction 2 |
|
Default |
Local VAT in ST or Triangulation |
Intra-Community Supply |
|
Ex-works |
Intra-Community Supply or |
Local VAT in SF or |
|
* Country-specific Authority Option |
||
This table shows country-specific transportation responsibility:
|
Pick Up (Ex-works) |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Authority Option in Ship From Country |
Tax Treatment |
|
|
Either or Ship From |
Chain Transaction 2 Chain Transaction 1 |
Domestic Supply in SF Intra-Community Supply |
|
Ignore or Ship To |
Chain Transaction 2 Chain Transaction 1 |
Intra-Community Supply Domestic supply in ST |
|
Authority Option in Ship To Country |
Impact |
|
|
Either or Ship To |
Triangulation Simplification not possible. |
|
|
Ignore or Ship From |
Triangulation Simplification is possible. |
|
The transaction type is specified in the XML input element <TRANSACTION_TYPE> which is used to identify how a transaction should be taxed. For more information, see Transaction Types.